COOPERATION
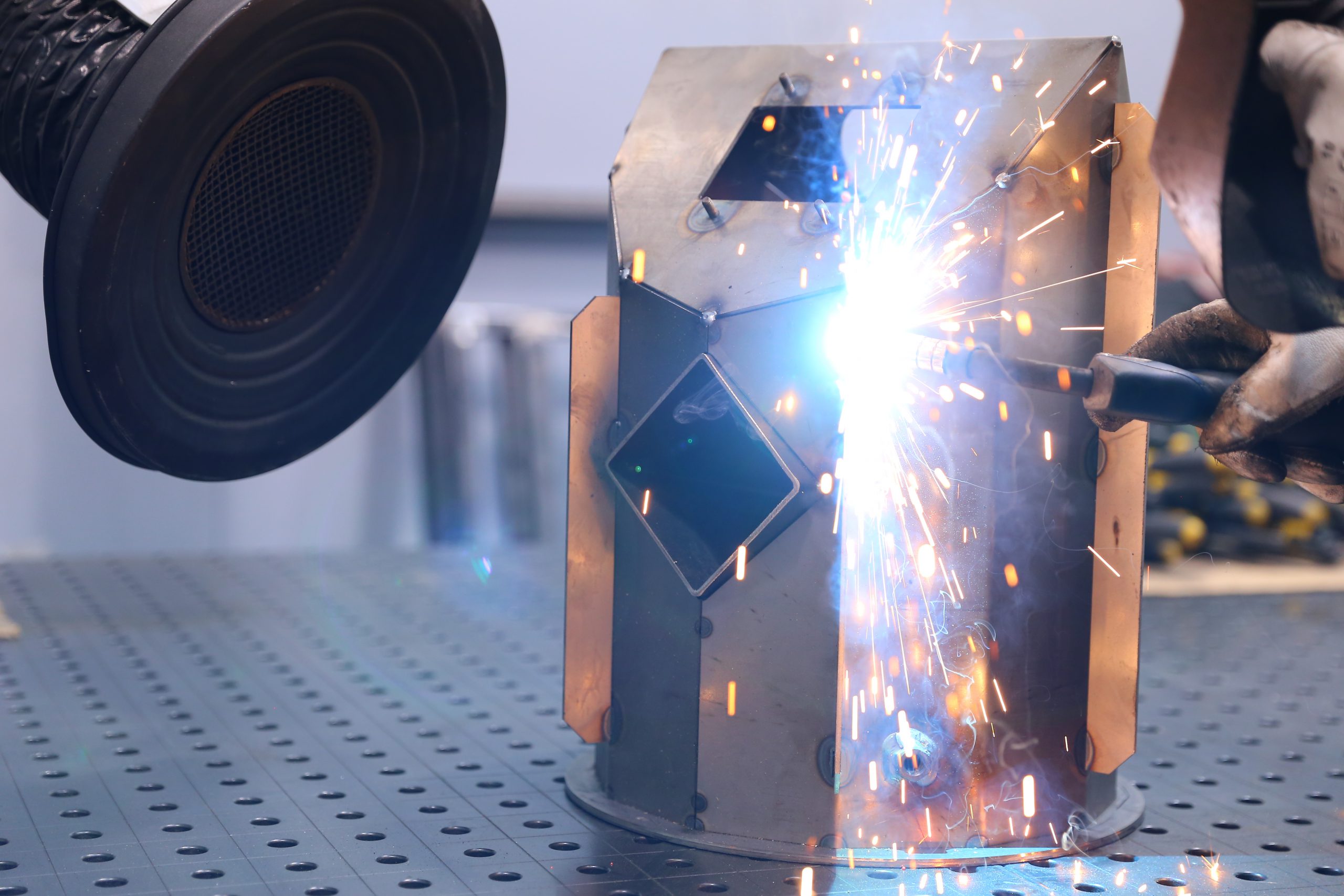
AUTOMATIC WELDING
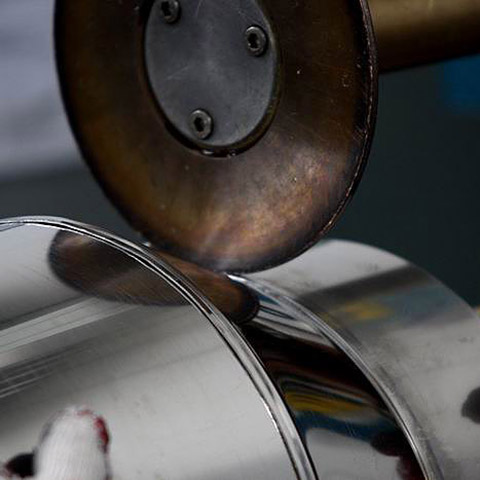
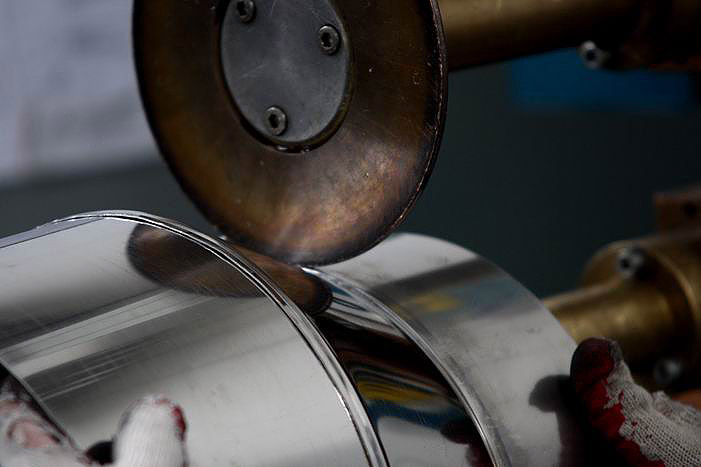
Fusion of metal parts as a result of heating and melting of material at the point of joining by means of an automatic welding robot. Automatic welding can be carried out with a fusible electrode or tungsten electrode.

The automatic welding process starts with the creation of a control program and a suitable holder for mounting the welded element on the table. After programming the robot, the operator places the welded element in the welding cell and closes the welding cell door. The robot joins the elements together with great accuracy.
| WELDING METHOD | MIG, TIG |
| SHIELD GAS | Argon |
| MAXIMUM WORKPIECE DIMENSIONS | 800 x 800 x 800* |
*depending on the detail