05.02.2020
WELDING
COOPERATION
WELDING
Merging of metal parts as a result of heating up and melting of the material at the point of joining. The source of heat is the welding arc. Welding takes place in a gas shielding, which has a direct impact on the efficiency and quality of welding.
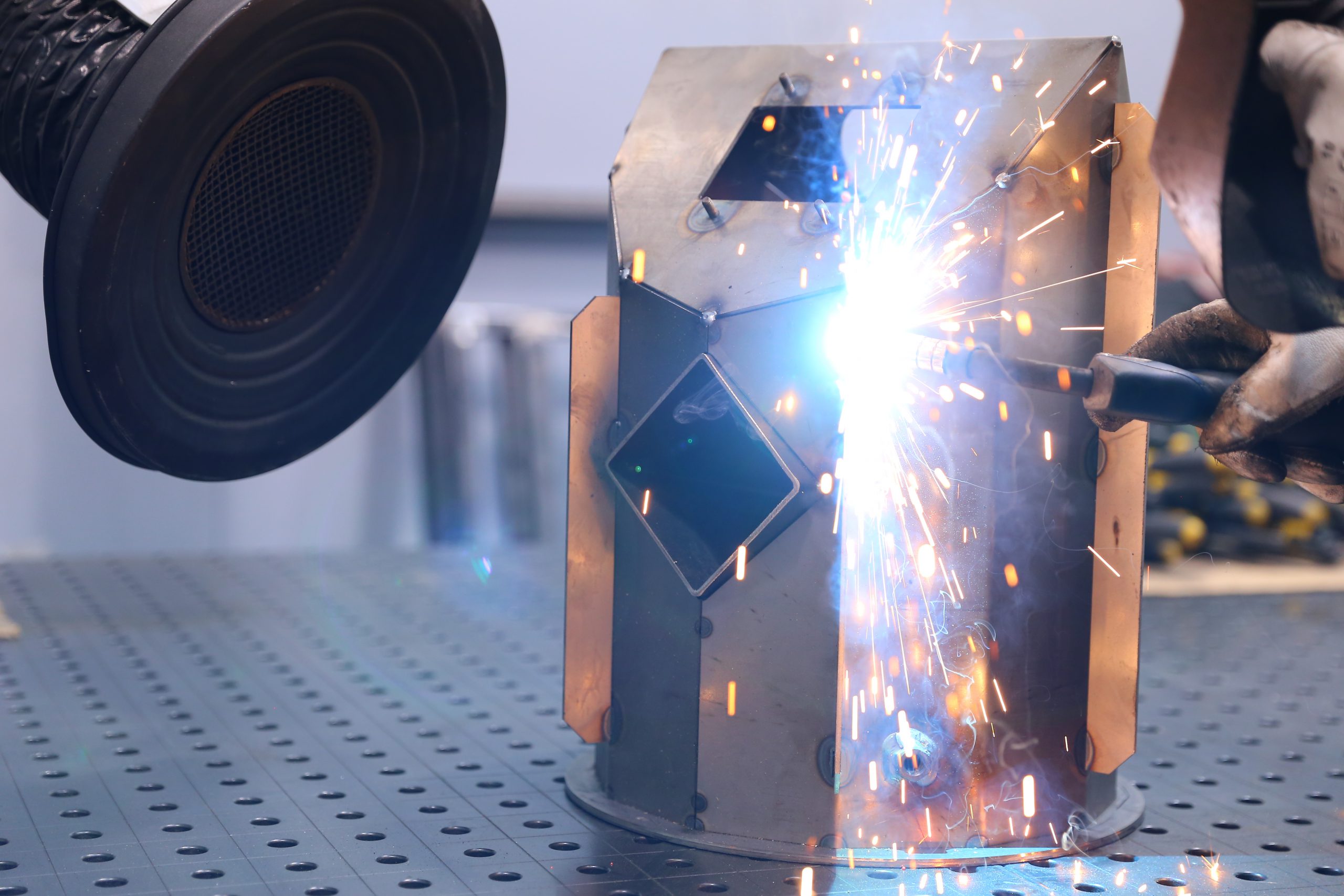
MIG/MAG (Metal Inert Gas / Metal Active Gas) – welding is a method of welding with a consumable electrode in an inert gas shield (MIG 131) or in an active gas shield (MAG 135), in which an electric arc glows between the electrode (as a wire) and the material being welded. This method is designed for the fusion of most materials (the appropriate electrode wire and shielding gas must be chosen).
TIG welding (Tungsten Inert Gas) – is a method of welding with an inert gas shielded tungsten electrode (argon, helium) in which an electric arc glows between the electrode and the material being welded. This method is designed for welding all types of steel (especially high-alloy steels and non-ferrous metals).
TIG welding
| WELDING METHOD | TIG |
| CURRENT ADJUSTMENT RANGE | 4- 300 A |
| SHIELD GAS | Argon |
| ELECTRODE DIAMETER | 1,6- 3,2 mm |
MIG/MAG welding
| WELDING METHOD | MIG/ MAG |
| SCOPE OF INTENSITY CONTROL | 50- 315 A |
| SHIELD GAS | Argon/ Corgon 10 |
| WELDING WIRE DIAMETER | 0,6- 1,2 mm |
Turntable
| TILT ANGLE OF THE TABLE | 0- 90° |
| DRIVE | Gearmotor – helical-worm gearbox |
| PURPOSE | Oval swivels |
| DIAMETER OF WELDED PARTS | 140- 370 mm |









